THC-O vs. Delta-8 vs. Delta-9 THC: What Are the Differences?

This article highlights the differences between THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC. You’ll learn everything about each compound, from its benefits and uses to safety and side effects, to their legal status.
Can’t wrap your head around different versions of THC?
From delta-8 to THC-O, cannabinoids from hemp are hot as lava right now.
But how do you tell the difference between THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC?
Which one is stronger? Are other THCs than delta-9 federally legal?
The research on THC-O dates back to as early as the 1940s, although we’re still learning about this cannabinoid. As it continues to gain popularity in the USA, it’s paramount to be on top of the facts — and how to find safe, effective, reliable THC-O extracts.
Here’s what you need to know about THC-O and how it differs from delta-8 and delta-9 THC.
THC-O vs. Delta-8 vs. Delta-9 THC (Summary)
- THC-O is an abbreviation for tetrahydrocannabinol acetate. It’s a semi-synthetic cannabinoid that can be extracted from hemp and marijuana.
- According to research, THC-O is 3x stronger than delta-9 THC and 6x stronger than delta-8 THC.
- THC-O comes with similar benefits to other THCs, but in much smaller doses.
- It’s critical to approach THC-O with caution because the higher potency increases the likelihood of side effects, such as anxiety, paranoia, and racing heart.
- THC-O is theoretically legal at the federal level, although this remains unclear since THC-O is considered a semi-synthetic compound.
- Watch out for contaminated and untested THC-O products. They may contain pesticides, heavy metals, mold, solvents, and more THC-O than declared.
What is THC-O and How is It Made?
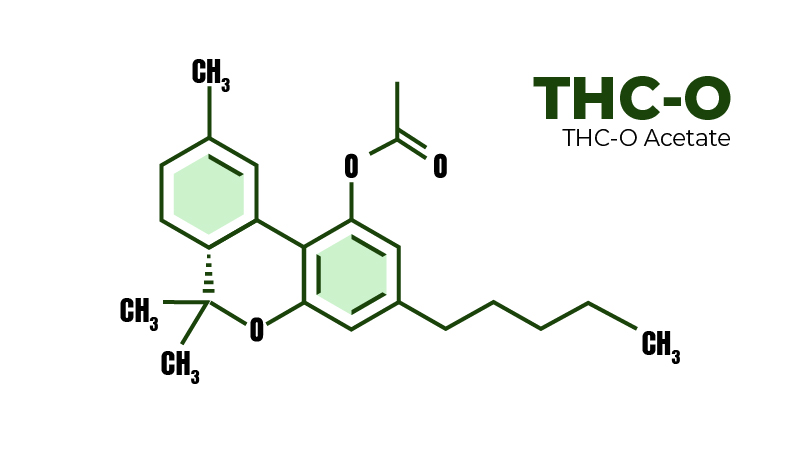
THC-O’s full name is THC-O acetate (1). It was made as a result of military experiments on non-lethal incapacitating drugs.
Researchers investigated its effects on dogs. At the end of the experiment, the dogs lost control of their motor functions and were extraordinarily high (2).
Today, manufacturers extract THC-O from hemp using a special conversion process. First, CBD is converted to delta-8 or another isomer. Then, they add Acetic Anhydride to the mix, creating THC-O.
CAUTION: do not use Acetic Anhydride at home. The compound is highly corrosive and flammable, putting your health, and safety in danger unless it’s handled in a lab. For this reason, we recommend buying THC-O products only from reputable sources that provide batch-specific lab reports.
Health Benefits
Not much is known about the benefits of THC-O, but judging from the pharmacology of delta-9 THC, it’s within reason to assume it comes with similar effects.
THC-O may:
- Curb inflammation
- Reduce pain
- Ease anxiety
- Reduce nausea and vomiting
- Lower stress
- Increase appetite
The effects of THC-O are dosage-dependent. Since THC-O is 3x as potent as delta-9 THC, start with a very low dose to see if you can reap the benefits without experiencing side effects.
Speaking of which…
Side Effects
Again, research on the safety and side effects of THC-O is scarce. We can only predict them by looking at the safety of delta-9 THC.
The side effects of THC-O include:
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Cold sweats
- Increased heartbeat
- Confusion
- Problems with coordination
- Short-term memory impairment
- Sedation
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- A drop in blood sugar levels (aka greening out)
How Do You Take THC-O?
The final form of THC-O looks like a viscous brown liquid. You can infuse it into edibles, vape oil, or dab it in a rig. Depending on the consumption method, the effects should kick in within 20-60 minutes.
What is Delta-9 THC?
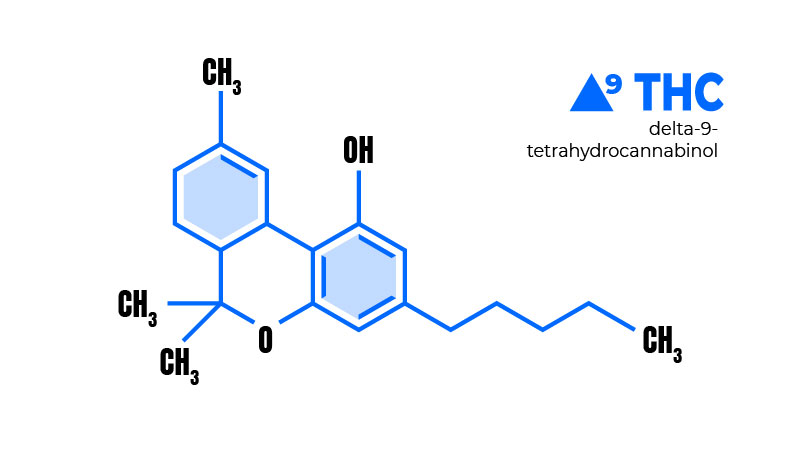
Delta-9 is the primary naturally-occurring intoxicant in cannabis plants. When the dose of delta-9 THC breaches your tolerance threshold, you get high.
In states where marijuana is legal for medical or recreational use, cannabis dispensaries offer delta-9 THC products in various forms, including brownies, cookies, candies, gummies, tinctures, vape pens, topicals, and beverages.
Health Benefits
Potential benefits of using delta-9 THC include (3):
- Decreased anxiety
- Increased appetite
- Relaxation
- Feelings of happiness and euphoria
- Improved sensory perception
- Heightened creativity
- Relief from pain and inflammation
- Neuroprotection
Studies have demonstrated that delta-9 THC may be a therapeutic agent in the treatment of nausea and vomiting, seizure disorders, muscle spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis (MS), insomnia, and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease (4, 5, 6, 7, 8).
While there’s still a need for more clinical trials on the health benefits of THC and its long-term effects on humans, patients using medical cannabis under a doctor’s supervision report significant improvements with only mild side effects that are usually dose-dependent.
Side Effects
Several factors come into play when it comes to side effects of THC, from one’s tolerance to the current state of mental health and consumption method.
The side effects of delta-9 THC include (9):
- Increased anxiety
- Paranoia
- Confusion
- Sedation
- Dry mouth
- Dry eyes
- Low blood pressure
- Feelings of unease
In some heavy cannabis users who take large doses daily, scientists have found an increased risk of cannabis hyperemesis syndrome, which involves stomach upset, nausea, and vomiting (10).
High-THC cannabis can also be risky for individuals with a genetic burden of psychiatric diseases, such as schizophrenia.
What is Delta-8 THC?
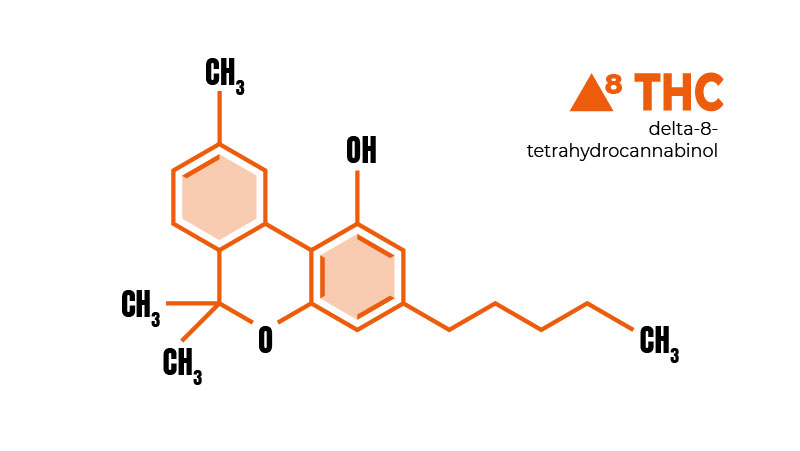
Delta-8 THC is an analog of delta-9 THC. It forms as a byproduct of THC’s oxidation. A large share of THC transforms into CBN when exposed to air and light, while only a fraction turns into delta-8 THC.
Because of that, manufacturers convert CBD into delta-8 THC, using heavy metal reagents and acids.
Delta-8 THC is about twice less potent as delta-9. It also comes with a lower incidence of anxiety and paranoia, making it a decent alternative for sensitive individuals.
You can find delta-8 THC products in many forms, including tinctures, gummies, vape carts, infused drinks, and pre-rolled joints.
Health Benefits
Similar to THC-O, the studies on the health benefits of delta-8 are few and far between. The best-researched areas include its effects on nausea, pain, neurodegeneration, and appetite.
The health benefits of delta-8 THC include:
- Pain relief
- Better sleep quality
- A calming effect on the nervous system
- Improved appetite
- Reduced inflammation
- Lower levels of anxiety
The risk and benefits of delta-8 THC are mostly dosage-dependent. Other driving factors include:
- The chemical composition of the product
- The method of administration
- The frequency of use
- The dose consumed
- Product Quality
- Demographic and health status of consumers
Side Effects
As with any natural compound, consuming more delta-8 THC than the body can handle may lead to short-term side effects, such as:
- Disorientation
- Dry mouth and eyes
- Increased heart rate
- Impaired coordination
- Lethargy
- Elevated anxiety
The adverse reactions shouldn’t last more than a couple of hours from inhalation or oral consumption.
Similar to delta-9 THC, delta-8 users with preexisting conditions or a burden of psychiatric diseases should approach these products with caution.
THC-O vs. Delta-8 vs. Delta-9 THC: What’s the Difference?
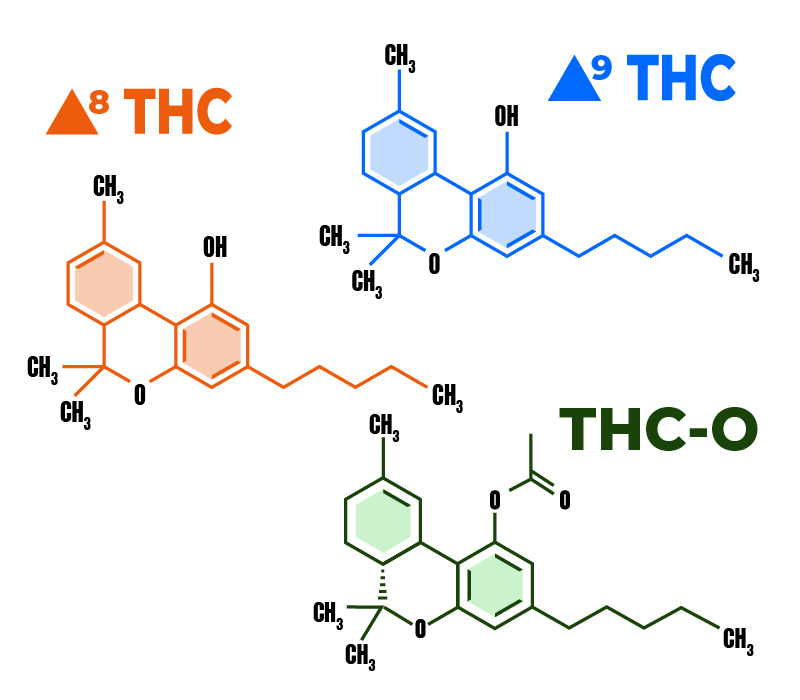
THC-O is stronger than both delta-8 and delta-9 THC.
Delta-8 is more mellow and less likely to trigger anxiety and paranoia. Users describe the effects as mellow, relaxing, or stimulating (depending on the product’s strain).
The effects of delta-9 THC are more cerebral and can drive the user into mental discomfort when consumed at large doses by low-tolerance individuals.
Since THC-O comes with a stronger psychedelic potential. Its effects may vary from person to person, but many users report having more spiritual experiences on the verge of hallucinations.
Below we elaborate on the most visible similarities and differences between THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC.
Similarities
All three compounds can produce psychoactive effects. They can be positive or negative depending on the dosage and the aforementioned personal factors.
The intoxicating effects of THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC stem from their interaction with the brain’s CB1 receptors.
The activation of these receptors can get you high, but it also comes with a range of therapeutic effects. That’s why THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC can relieve pain, protect and heal nerves, improve appetite, and reduce the symptoms of depression.
They also interact with CB2 receptors in the immune system, hence the anti-inflammatory effect.
Last but not least, THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC are available in similar formats, including tinctures, vapes, edibles, beverages, and flowers.
Differences
Aside from the potency, THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC differ in the following aspects:
Research Availability
Scientists have been studying delta-9 THC extensively for almost 60 years, but we know very little about delta-8 and THC-O.
We can judge the safety and side effects of delta-8 and THCO by looking at the research regarding delta-9 — but there’s a need for more human trials to draw any conclusions.
Extraction Methods
Delta-9 THC is directly extracted from marijuana plants. A crude THC extract contains all phytochemicals that naturally occur in cannabis, including terpenes, flavonoids, essential oils, and waxes.
From there, it can be further purified and turned into sauce, distillate, isolate, and other concentrates.
Delta-8 and THC-O products are made using a complex conversion process from CBD. This is necessary for extracting usable amounts of these cannabinoids from hemp. Otherwise, the manufacturing process would be cost-prohibitive.
Legal Status of THC-O, Delta-8, and Delta-9 THC

Another major difference between THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC is their legal status.
Delta-9 from hemp is heavily regulated at the federal level. So far, only 17 states have legalized its recreational use, and almost every state has some kind of medical marijuana program.
With delta-8 and THC-O, it’s a different story because they’re theoretically legal at the federal level.
The 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp and its derivatives, including cannabinoids, terpenes, isomers, and salts — as long as the final product contains 0.3% delta-9 THC or less.
Delta-8 and THC-O products meet the above criteria, but there’s a debate about their legal status in individual states. Some states banned all synthetic extraction methods, while others carried over the 0.3% limit to other forms of THC, making delta-8 and THC-O products illegal.
Check up on our local Delta 8 state laws if you want to learn more about the legality of this specific cannabinoids.
How to Safely Buy THC-O Products
Since THC-O is largely unregulated, there’s a high risk involved in buying from unverified sources. According to cannabis researcher James Stephens, producers don’t even know or claim to not know what’s inside their products.
Many THC extracts out there are contaminated with sketchy additives that can be detrimental to your health.
You want to buy from a reputable company that provides batch-specific lab reports for each product and has a well-documented record of returning customers.
The best way to find high-quality THC-O products is to order from CBD companies that are now expanding their line-up with such extracts. They know how to grow hemp, process it, and ensure that the end product is safe for consumers.
Can THC-O, Delta-8, and Delta-9 THC Show Up On a Drug Test?
Delta-9 THC can show up on a drug test. In fact, it’s the most commonly tested illicit substance in workplace drug screenings.
But what about delta-8 and THC-O? Can they, too, make you fail a drug test?
Unfortunately, yes.
Even though they have slightly different molecular structures, both compounds interfere with testing for THC in presumptive and definitive urine drug tests.
Key Takeaways on the Differences Between THC-O, delta-8, and delta-9 THC
THC-O is the new psychoactive cannabinoid on the block. Although it was discovered in the 1940s, there wasn’t much noise around it until the recent boom on hemp-derived psychoactive cannabinoids.
The potency of THC-O is measured three times as high as that of delta-9 THC, so it’s wise to exercise caution if that’s your first contact with this compound.
Although THC-O has similar health benefits to other THCs, its strength increases the likelihood of side effects like paranoia, anxiety, dizziness, confusion, and a racing heart.
The THC-O market remains largely unregulated. If you want to buy it safely, opt for reputable manufacturers who provide relevant lab reports for potency and purity, and a high level of transparency.
Sources:
- Holt, A. K., Poklis, J. L., & Peace, M. R. (2022). Δ8-THC, THC-O Acetates and CBD-di-O Acetate: Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoids Found in Commercially Sold Plant Material and Gummy Edibles. Journal of analytical toxicology, bkac036. Advance online publication. [1]
- National Research Council (US) Panel on Anticholinesterase Chemicals; National Research Council (US) Panel on Anticholinergic Chemicals. Possible Long-Term Health Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Chemical Agents: Volume 1 Anticholinesterases and Anticholinergics. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1982. 1, INTRODUCTION.
- Webb, C. W., & Webb, S. M. (2014). Therapeutic benefits of cannabis: a patient survey. Hawai’i journal of medicine & public health : a journal of Asia Pacific Medicine & Public Health, 73(4), 109–111.
- Parker, L. A., Rock, E. M., & Limebeer, C. L. (2011). Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids. British journal of pharmacology, 163(7), 1411–1422.
- Markovà, J., Essner, U., Akmaz, B., Marinelli, M., Trompke, C., Lentschat, A., & Vila, C. (2019). Sativex® as add-on therapy vs. further optimized first-line ANTispastics (SAVANT) in resistant multiple sclerosis spasticity: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial. The International journal of neuroscience, 129(2), 119–128.
- Babson, K. A., Sottile, J., & Morabito, D. (2017). Cannabis, Cannabinoids, and Sleep: a Review of the Literature. Current psychiatry reports, 19(4), 23. [2]
- Yenilmez, F., Fründt, O., Hidding, U., & Buhmann, C. (2021). Cannabis in Parkinson’s Disease: The Patients’ View. Journal of Parkinson’s disease, 11(1), 309–321. [3]
- Kim, S. H., Yang, J. W., Kim, K. H., Kim, J. U., & Yook, T. H. (2019). A Review on Studies of Marijuana for Alzheimer’s Disease – Focusing on CBD, THC. Journal of pharmacopuncture, 22(4), 225–230.
- Adverse effects of cannabis. (2011). Prescrire international, 20(112), 18–23. [4]
- Galli, J. A., Sawaya, R. A., & Friedenberg, F. K. (2011). Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. Current drug abuse reviews, 4(4), 241–249. [5]