What is CBDv (Cannabidivarin)?
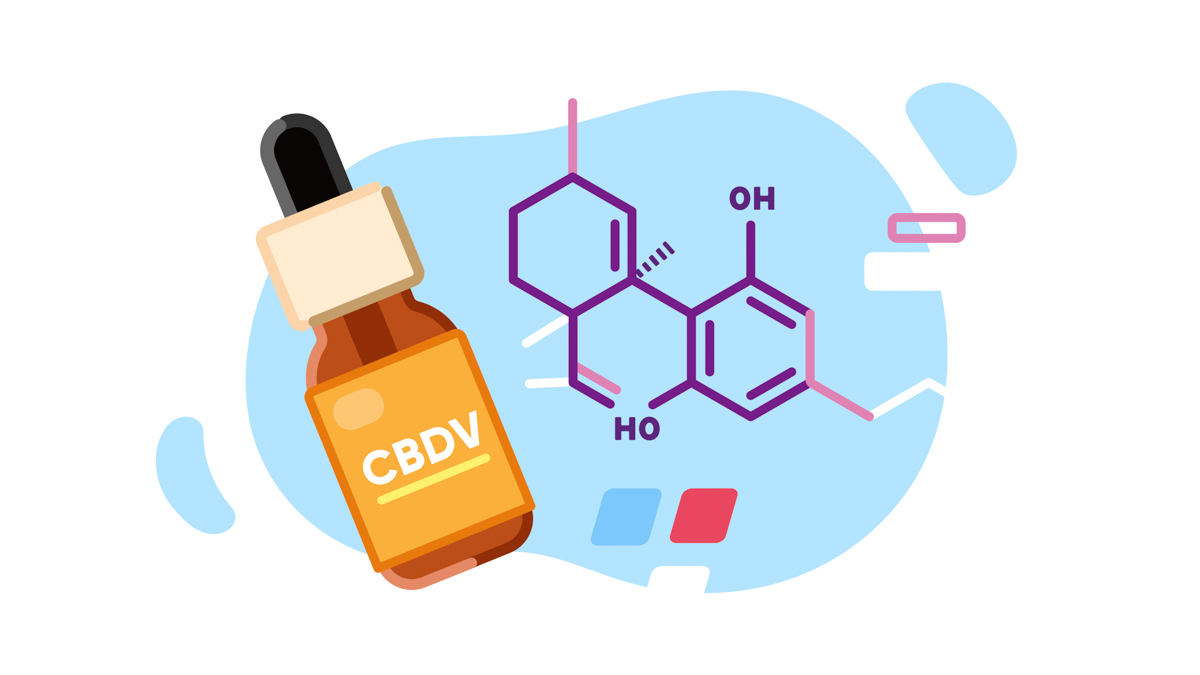
This article focuses on CBDv (cannabidivarin), a non-psychotropic minor cannabinoid that contributes to the entourage effect by lending it its unique health benefits. We touch down on the chemical properties of CBDv and its therapeutic effects. We also shed light on current research regarding the medical use of CBDv. After reading this article, you’ll learn how to use CBDv in your routine and where to find high-quality products.
The cannabis plant is a powerhouse of therapeutic compounds, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids.
There are at least 150 cannabinoids, and as researchers discover more such molecules, the interest in their medical uses increases proportionately.
CBDv has been gaining a lot of traction in recent years, although it’s not as abundant as CBD or THC. The cannabinoid was discovered in the late 1970s, but until then, scientists haven’t given it as much attention as it deserves.
But what exactly is CBDV? And what is its role in modulating the effects of cannabis?
Keep reading to find out.
What is CBDv?
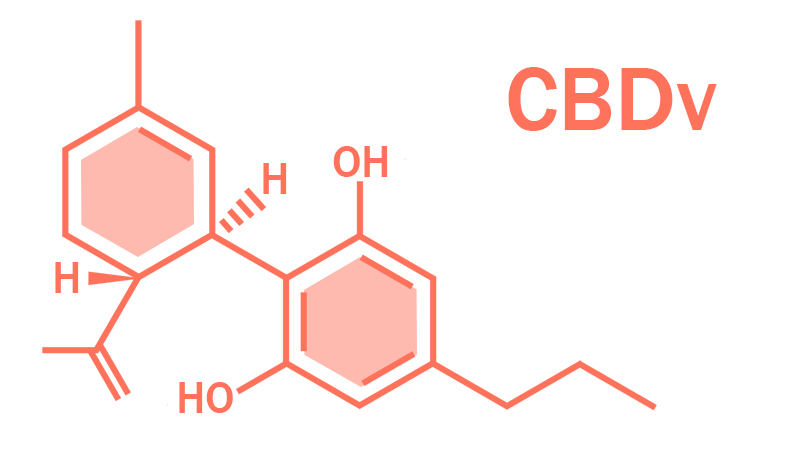
CBDv is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid that won’t get you high like THC. It has a similar molecular structure to CBD. Both compounds have 7 double-bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers, and the only difference is that CBDv comes with a propyl chain.
However, unlike CBD, CBDv occurs in much smaller concentrations in hemp plants, so its extraction is more expensive. If you’re looking for strains high in CBDv, opt for Indica Landrace strains.
CBDv belongs to a group called “varin” cannabinoids.
Here’s what you should know about them.
Related: What Is CBD (Cannabidiol)?
A Word on Varin Cannabinoids
Varin Cannabinoids is a term for cannabinoids that have “v” at the end of their names, such as CBDv, CBDGv, DCBCv, and THCv.
They’re classified as a subfamily of cannabinoids that come with three carbons. The major cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC, have five carbons, but there are also other cannabinoids with fewer carbons on their alkyl side.
The number of carbons is essential for determining which receptors the cannabinoids will bind to and what type of effects they will produce. The longer the chain, the more intense the effects.
How is CBDv Extracted?
The direct extraction of CBDv can be costly, so scientists often make it by using cellular agriculture, which is a type of biotechnology utilized in food production.
This method ensures the highest amount of CBDv, which is then used for medical research. Since the studies on CBDv are in their infancy, there are not many CBDv-infused products on the market, but this will change sooner than later.
How Does CBDv Work?
Now that we explained what CBDv is, it’s time to shed light on its mechanisms of action. As mentioned earlier, CBDv has a similar structure to CBD, and both compounds produce similar effects on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and TRP Ion Channels.
What is the ECS?
The ECS is the master regulatory network in humans that connects to other systems and organs with two types of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2). It controls essential functions like sleep, immune response, pain perception, appetite, body temperature, fertility, mood, memory, etc.
The ECS produces its own cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) that bind to these receptors and produce a range of therapeutic effects, helping the body return to homeostasis (balance).
Phytocannabinoids, like CBDv, CBD, and THC, modulate the activity of the ECS, providing it with unique health benefits.
What Are Ion Channels
Ion Channels have a sensory role in the body and signal the nervous system about the presence of chemicals and extremely hot and cold temperatures. Your body activates them when you eat spicy food.
CBDv, along with CBD, aids certain TRP channels, making them potentially effective agents for treating neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and migraines. CBDv has anecdotally a much greater impact on TRP channels than other cannabinoids in hemp.
CBDv Effects & Benefits
Since CBDv comes with a similar chemical structure to CBD, it produces many of the same effects.
However, CBDv is said to have remarkable anticonvulsant and pain-relieving effects. They’re mediated by the capsaicin receptor TRPV1.
This interaction grants CBDv anti-epileptic properties and is often researched for its ability to treat seizures. The cannabinoid also activates the TRPA1 and TRPV2 ion channels that reduce the excitability of the nervous system.
CBDv can be used for muscle recovery, chronic pain, stress, and anxiety.
Let’s look closely at the studies regarding the health benefits of CBDv.
Studies on CBDv
CBDv has recently garnered a lot of attention from the medical community, mainly thanks to its antiepileptic and pain-relieving properties.
Here’s what studies have found to date.
CBDv for Childhood Epilepsy
Childhood treatment-resistant epilepsy is one of medical researchers’ main areas of interest. GW Pharmaceuticals, a pharmaceutical company from the U.K., paved the way for studies on this novel cannabinoid, and there’s been promising evidence that CBDv can stop chemically-induced seizures (1). However, this study was conducted on animals. Now GW Pharmaceuticals is investigating CBDv’s potential in treating autism spectrum disorder.
CBDv as Anticonvulsant
A 2012 study published in the British Journal of Pharmacology concluded that CBDv had significant anticonvulsant effects on rats and mice. However, the cannabinoid doesn’t affect regular motor functions (2).
The journal Translational Psychiatry published the effects of a study on using CBDv for autism spectrum disorder in 2019, and they accidentally discovered that this natural compound curbs PTZ seizure activity (3).
Another study conducted in 2018 showed that CBDv and CBD influenced the activity of TRPV1 receptors (4). A recent 2019 study found that CBDv can help with dysfunctional social behaviors, although the study was again performed on mice (5).
CBV and Autism Spectrum Disorder
Since autism is an incurable disorder, people are looking for treatments that can ease the symptoms and improve the quality of life. CBDv has been found to be effective in reducing such symptoms and easing acute anxiety by modulating the neurotransmitters’ activity, such as glutamate and GABA. Furthermore, CBDv may help increase anandamide levels in the brain, which have been found to be lower in people with an autism spectrum disorder.
CBDv for Nausea
Animal-based studies also explored the effects of CBDv on toxin-induced nausea. Knowing that the nausea response is regulated by the endocannabinoid system, stimulating the ECS can reduce the symptoms and prevent vomiting.
Another important study from the British Journal of Pharmacology found that CBDv is an agonist of the CB1 receptor and inhibits nausea (6).
CBDv for Duchene Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
DMD is a disease where the skeleton and muscle suffer from damage caused by inflammation, so scientists wanted to find if CBDv can be a potential treatment.
A study from the BMJ showed that CBDv not only curbed inflammation but also improved muscle function, leading to faster recovery (7).
Another study published by The National Research Council in Italy also found that CBDv and CBD improve DMD. The authors concluded that both cannabinoids could restore the functions of compromised muscle stem cells, but higher doses are required to achieve that (8).
CBDv for Rett Syndrome
Rett Syndrome is a genetic, incurable condition, meaning that treatments can only reduce the severity of symptoms and improve overall life quality in patients.
A study published in Neuropsychopharmacology demonstrated that CBDv is able to restore memory deficiencies in mice that have the same problems as humans who suffer from Rett syndrome (9).
In another study from the journal Pharmacological Research, CBDv was found to reduce gastrointestinal inflammation that often derives from other diseases (10). This study was based on animals, specifically mice, so we need more human trials to find out whether CBDv can improve motor coordination and sociability deficits and normalize excess brain weight.
What’s the Link Between CBDv & Big Pharma?
CBDv has sparked the attention of Big Pharma recently. GW Pharmaceuticals ran one of the studies, which aimed to develop a synthetic analog of this cannabinoid called “GWP42006.” GW Pharmaceuticals was trying to find a treatment for childhood epilepsy, so they put the compound under clinical trials.
Even though their 2018 study showed no difference between individuals with seizures who took CBDv and those who didn’t, the study pushed researchers further to explore what benefits CBDv could have for Rett syndrome, autism, and other conditions.
Subsequent studies showed that CBDv affects the capsaicin receptors that control the progression of several types of seizures, suggesting that previous works could’ve used too small doses.
Recently, a European Medicine Agency (EMA) study concluded that CBDv could be used for Rett syndrome and Fragile X. In 2020, the FDA approved CBDv as a treatment for these syndromes, and the cannabinoid is still studied for autism spectrum disorder.
Is CBDv Safe?

So far, no adverse effects have been reported for CBDv. However, that doesn’t mean there are no adverse reactions at all.
CBDv is still in clinical trials, so although some researchers claim it’s better tolerated than other cannabinoids, it may still produce common side effects like dry mouth, changes in appetite, dizziness, and diarrhea. We need more human studies to elaborate on the safety profile of CBDv.
How to Use CBDv
Because CBDv isn’t an officially approved medication, there are no dosage guidelines on using CBDv for any health condition.
Currently, you’ll find higher levels of CBDv in Landrace cannabis strains. Other than that, the cannabinoid is rare and must be often isolated in a laboratory.
However, as manufacturers explore different options for extracting minor cannabinoids from cannabis, we may soon witness the surge of CBDv products in similar formats to CBD and THC — including oils, capsules, edibles, topicals, vapes, and more.
CBDv-rich Strains
If you’re looking for cannabis strains that are high in CBDv, look for varieties from Africa and Asia that are more dominated by the Indica lineage.
The following cannabis strains have been bred to contain higher levels of CBDv than average:
- Dance World
- Euphoria
- Royal Medic
- Royal CBDv
- CBDv Auto
- CBD-Victory
Where to Buy CBDv
There aren’t many CBDv products on the market these days because CBDv isn’t as popular as other cannabinoids. A lion’s share of the CBDv space is made from CBDv isolate, which is the easiest form of CBDv to extract.
You can find CBDv isolate in cannabis dispensaries, specialized CBD stores, and online retailers.
CBDv vs. CBD: What’s the Difference?
CBDv has only a slightly different chemical structure than CBD. Although there’s not enough conclusive evidence, both cannabinoids share many common benefits, especially for pain, seizures, inflammation, and neurodegeneration.
These are just rumors, but some scientists and experts believe that CBDv can provide better results for mood disorders, nausea, and digestive health.
CBDv is like a sibling to CBD, but it has stronger effects on certain brain receptors.
Key Takeaways on CBDv
As you can see, CBDv offers several interesting benefits, some of which may be even more pronounced than with the major cannabinoids like THC and CBD.
Although CBDv isn’t as well researched as the two above cannabinoids, it’s a promising compound for treating nausea, seizures, pain, inflammation, mood disorders, and gut issues.
Still, these are just preliminary studies that have been conducted mostly on mice. We need more human trials until CBDv is accepted as a remedy for any of the said conditions.
Let’s hope that extractors will come up with efficient ways to produce CBDv from hemp, making it more available for regular folks so that we also have some real-life evidence to share.
Sources:
- Amada, N., Yamasaki, Y., Williams, C. M., & Whalley, B. J. (2013). Cannabidivarin (CBDV) suppresses pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced increases in epilepsy-related gene expression. PeerJ, 1, e214. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.214
- Hill, A. J., Mercier, M. S., Hill, T. D., Glyn, S. E., Jones, N. A., Yamasaki, Y., Futamura, T., Duncan, M., Stott, C. G., Stephens, G. J., Williams, C. M., & Whalley, B. J. (2012). Cannabidivarin is anticonvulsant in mouse and rat. British journal of pharmacology, 167(8), 1629–1642. [1]
- Pretzsch, C.M., Voinescu, B., Lythgoe, D. et al. Effects of cannabidivarin (CBDV) on brain excitation and inhibition systems in adults with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): a single dose trial during magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Transl Psychiatry9, 313 (2019).
- Muller, C., Morales, P., & Reggio, P. H. (2019). Cannabinoid Ligands Targeting TRP Channels. Frontiers in molecular neuroscience, 11, 487. [2]
- Zamberletti E, Gabaglio M, Piscitelli F, et al. Cannabidivarin completely rescues cognitive deficits and delays neurological and motor defects in male Mecp2 mutant mice. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2019;33(7):894-907. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881119844184
- Rock, E. M., Sticht, M. A., Duncan, M., Stott, C., & Parker, L. A. (2013). Evaluation of the potential of the phytocannabinoids, cannabidivarin (CBDV) and Δ(9) -tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), to produce CB1 receptor inverse agonism symptoms of nausea in rats. British journal of pharmacology, 170(3), 671–678. [3]
- Iannotti, F. A., Pagano, E., Moriello, A. S., Alvino, F. G., Sorrentino, N. C., D’Orsi, L., Gazzerro, E., Capasso, R., De Leonibus, E., De Petrocellis, L., & Di Marzo, V. (2019). Effects of non-euphoric plant cannabinoids on muscle quality and performance of dystrophic mdx mice. British journal of pharmacology, 176(10), 1568–1584. [4]
- Iannotti, F. A. (2019). Pharmacological Actions and Potential Therapeutic Use of Cannabinoids in Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy. In (Ed.), Muscular Dystrophies. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85131
- Vigli, D., Cosentino, L., Raggi, C., Laviola, G., Woolley-Roberts, M., & De Filippis, B. (2018). Chronic treatment with the phytocannabinoid Cannabidivarin (CBDV) rescues behavioural alterations and brain atrophy in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Neuropharmacology, 140, 121–129. [5]
- Pagano, E., Romano, B., Iannotti, F. A., Parisi, O. A., D’Armiento, M., Pignatiello, S., Coretti, L., Lucafò, M., Venneri, T., Stocco, G., Lembo, F., Orlando, P., Capasso, R., Di Marzo, V., Izzo, A. A., & Borrelli, F. (2019). The non-euphoric phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin counteracts intestinal inflammation in mice and cytokine expression in biopsies from UC pediatric patients. Pharmacological research, 149, 104464.